The Overlooked Choice of Exterior Wall Insulation Materials
In many construction projects, Exterior Wall Insulation Board materials tend to be limited in variety. This is often due to insufficient consideration by contractors, who typically select Insulation Materials based on short-term cost control rather than long-term performance and economic benefits. As a result, the selection of insulation materials often fails to align with the ongoing advancements in energy-efficient construction technologies. Additionally, some manufacturers remain hesitant or skeptical about emerging insulation materials, resisting change and failing to keep pace with the evolving industry landscape

Advantages of Exterior Wall Insulation Technology
- Wide Application & Comprehensive Insulation Exterior Wall Insulation: technology is widely applicable, providing effective thermal insulation not only for specific parts of a building but for the entire structure. It helps maintain stable indoor temperatures, making it suitable for both cold and warm climates.
- Enhanced Protection Against Environmental Factors: By adding a protective insulation layer to the external walls, buildings gain improved resistance to UV exposure, wind, frost, rain, and snow, reducing direct damage to the structure. This also helps prevent water infiltration between building layers, minimizing long-term maintenance costs.
- Thermal Bridge Elimination: Proper insulation placement can effectively eliminate thermal bridges, preventing heat loss at weak points such as building joints and balconies, ensuring better energy efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency & Indoor Comfort: Exterior wall insulation systems not only help regulate indoor and outdoor air temperatures but also significantly reduce heat transfer from external walls. This leads to lower energy consumption, creating a more comfortable indoor environment and enhancing overall occupant satisfaction.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Boards: Widely used due to affordability, EPS has a thermal conductivity of approximately 0.041 W/(m·K). However, it offers limited fire resistance and mechanical strength, and installation can be labor-intensive.
- Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) Boards: Featuring lower thermal conductivity and good compressive strength, XPS is less permeable but may have adhesion issues with certain substrates.
- Glass Wool: Comprising fibrous materials with thermal conductivity ranging from 0.030 to 0.045 W/(m·K), glass wool provides sound absorption and fire resistance.
- Phenolharzschaumplatten: With a thermal conductivity of about 0.020 W/(m·K), phenolic foam offers excellent insulation and fire resistance.
- Polyurethane Foam Board (PU): Known for superior performance, PU foam has a thermal conductivity of approximately 0.020 W/(m·K) and excellent moisture resistance, making it ideal for roofing and below-grade applications.
- Indoor temperature stability improved, with fluctuations reduced from ±1.5°C to ±0.5°C.
- System failure rates dropped by 40%, lowering annual maintenance costs by 18%.
- These changes substantially reduced operational expenses, highlighting the superior performance of advanced insulation materials and equipment in HVAC applications.
- Clean wall surfaces thoroughly to remove dust and debris, ensuring optimal insulation adhesion.
- Apply a leveling plaster to create a smooth and even surface.
- Develop a construction plan based on local climate and building type to ensure conditions are suitable for installation.
- Consider building structure, climate, and environmental factors to determine the appropriate insulation material, installation method, and thickness.
- Use eco-friendly materials to support sustainable development.
- Regularly inspect wall flatness to ensure insulation materials adhere properly.
- Pay special attention to critical areas such as corners, windows, and doors to prevent gaps, cracks, or detachment.
- Seal all joints to eliminate air leakage and moisture infiltration.
- Choose low thermal conductivity materials to prevent heat loss.
- Utilize insulated materials that reduce cooling and heating loads for improved energy efficiency.
- Integrate smart temperature control systems to optimize building performance.
- Monitor material composition and coating thickness to maintain quality standards.
- Ensure proper sealing at wall corners and connection points to avoid defects.
- Follow environmental regulations by selecting sustainable and non-toxic materials.

Selecting and Applying High-Performance Insulation Materials
Exterior wall insulation materials can be categorized into several types:
Each material has distinct advantages and limitations, making it crucial to select the right insulation based on specific project requirements. For example, while EPS is affordable and widely used, its fire resistance is poor; XPS has excellent thermal performance but lacks breathability; Glass wool offers good fire resistance but requires careful moisture control; Phenolharzschaumplatte provides strong insulation, but quality varies by manufacturer; and PU foam Insulation Board delivers top-tier performance but comes at a premium cost.

Insulation Materials in Engineering Applications: A Real Case Study
In an earlier GFI Duct project, a client switched from traditional glass wool to Polyurethane Insulation. As a result, the wall’s thermal conductivity improved from 0.04 W/(m·K) to 0.024 W/(m·K), significantly enhancing the building envelope’s thermal efficiency and reducing heat loss.
According to the client’s final feedback:
While insulation materials played a critical role in these achievements, proper construction methods and quality control were equally important.
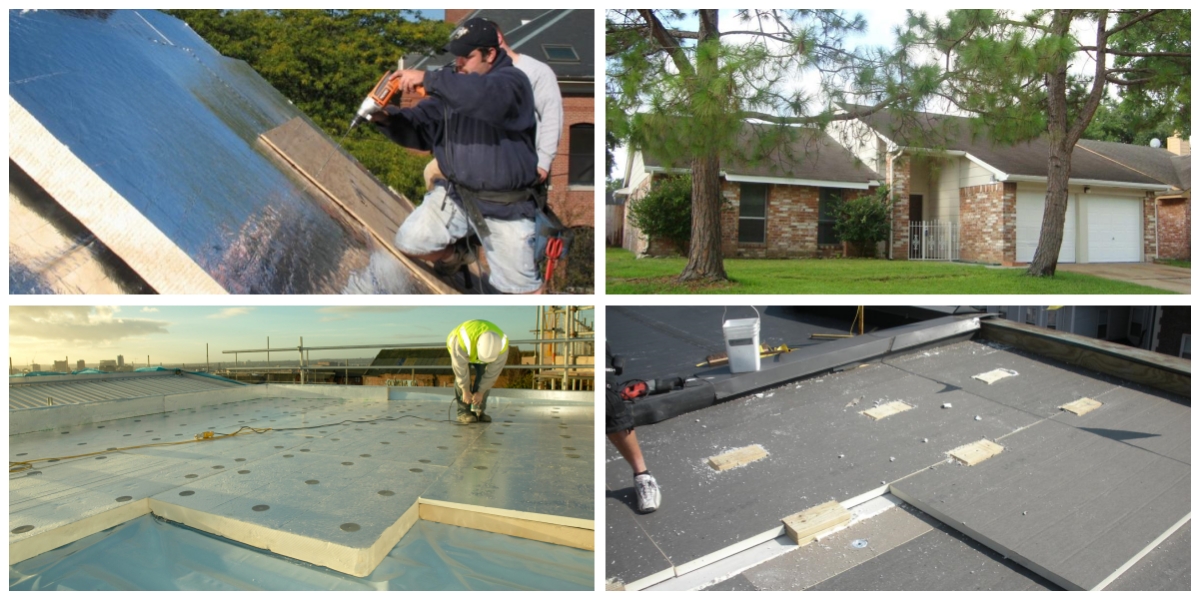
Best Practices for Exterior Wall Insulation Construction
1. Preparation Before Construction
2. Optimizing Construction Design
3. Quality Control During Construction
4. Enhancing Energy Efficiency
5. Attention to Detail

Abschluss
With advancements in energy-efficient technologies, the adoption of high-performance insulation materials is essential for improving building thermal efficiency und reducing long-term operational costs. As the global construction industry continues to emphasize energy conservation, buildings utilizing polyurethane and other advanced insulation materials will achieve superior energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and reduced maintenance costs.
By implementing precise insulation design and strict quality control, Exterior Wall Insulation projects can maximize performance and sustainability, contributing to the advancement of green building initiatives.
GFI Duct’s polyurethane and phenolic insulation boards offer exceptional thermal efficiency, low thermal conductivity, superior moisture resistance, and long-term durability, providing high-performance energy-saving solutions for global markets that demand eco-friendly and efficient building materials.




